Setting up a WordPress online store with the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress is something I do all the time. As a verified WooCommerce expert, I often get asked questions. There are a few common ones that are prefaced with, “This might be a stupid question”.
I don’t think there’s such a thing as a stupid question and it’s worth it to ask for an answer.
That’s why I’d like to answer three of the most common WooCommerce questions. I’m all about helping in the best way I can so here are the answers to these great questions.
What Happens When a User Account is Created?
This question gets asked a lot. User roles are a set of permissions given to a user of a WordPress site or WordPress online store.
There are several different levels of user roles and each one has certain capabilities assigned to them. These range from being able to leave a comment to editing pages or posts and other crucial settings.
If you give registered users inappropriate roles, they can have too much access to your website. They could make changes you don’t want. If not set properly, user roles are a security risk.
It’s easy to panic once you find this out. It can make you wonder what user role is set when a visitor registers for an account on your site.
Fortunately, user registration isn’t enabled in WordPress by default. Only accounts you manually add will have a user role and access to your site’s settings in part or totally.
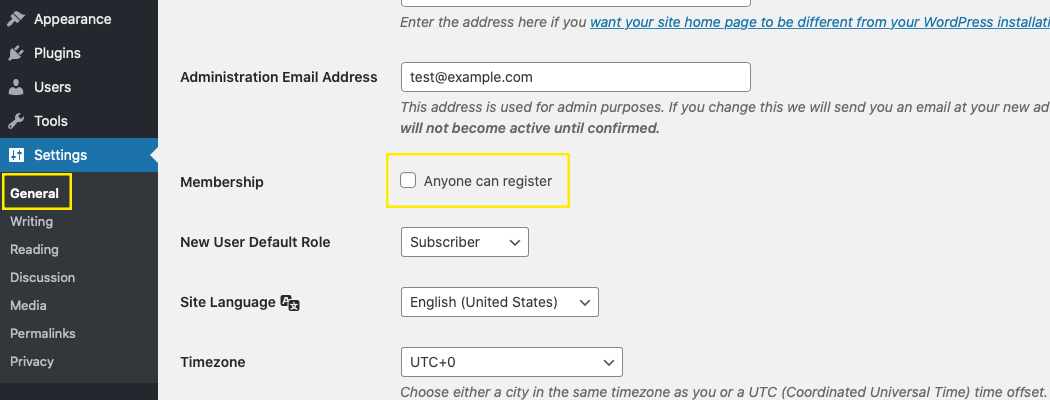
To turn registration on, you need to log into your site. Then, in your admin dashboard, go to Settings > General.
Check the Anyone can register box, then click Save Changes at the bottom of the page.
WordPress User Roles You Can Appoint
To properly answer this question, it’s crucial to first understand what user roles are available.
For WordPress websites, here are the core user roles that can be assigned:
- Subscriber – These users can comment on your site and edit their personal profile.
- Contributor – Users with this role can create and edit their own posts in addition to having the same capabilities as subscribers, but they can’t upload media or delete posts.
- Author – These users have the same capabilities as contributors, but they’re also able to upload media and publish as well as delete their own posts even after they have been published.
- Editor – An editor can do everything an author can, and can also add, edit and publish other users’ posts as well as pages. Editors can also manage comments, media, categories and tags.
- Admin – The administrator has all capabilities and has complete access to manage the entire site.
- Super admin – This user role applies to WordPress Multisite and not single installations. A super admin has admin capabilities for all sites in a network and not just for one site as an admin would. They can also manage all network-level settings.
When a visitor registers for an account on a WordPress site, they’re automatically assigned to the subscriber user role.
Additional WordPress Online Store User Roles
If you want to build or have a WordPress online store, there may be additional user roles available.
It can vary from plugin to plugin, but for the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress, there are these additional user roles that are included:
- Customer – A Customer can edit their account details such as their name and address. They can also review past and present orders.
- Shop manager – This user role has the capabilities of the customer user role as well as the editor role mentioned earlier. They can also view reports and manage all WordPress online store settings including creating, and editing products. But, they don’t have access to any other settings in the admin dashboard that the admin or super admin would be able to access.
A visitor is assigned the customer user role when they register for an account at checkout if you’re using the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress.
The WordPress admin user role also has the following capabilities added when the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress is installed:
- All WordPress online store settings and options can be managed including being able to add, and edit products.
- They’re also able to view reports.
What Happens When a Product is Added in WooCommerce?
When you’re using the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress and a product is published, it gets added to the “shop” page in a grid-style layout by default. The products are displayed as thumbnail images with basic details such as the price and product’s name.
Depending on the type of theme you have installed, products may be displayed differently.
When a product on that page is clicked, the user is directed to the full product page.
If you added a product to a category or multiple ones, then the product is also displayed on the corresponding category store pages. The same also applies if you include tags to the product. In this case, they’re shown on each tag’s page that’s used.
WooCommerce Plugin for WordPress Product Types
Beyond that, it depends on the type of product you created.
If you’re using the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress, here are the types of products and what happens when you add them:
- Simple – These are most products that need to be shipped. They’re displayed with shipping options when checking out such as a shipping calculator, dimensions, shipping options, and similar fields.
- Grouped – A collection or group of simple products that can be purchased individually or as a set. This option gives customers the convenience of only having to add one item to the cart. This is instead of having to edit the quantity or add a product multiple times.
- Virtual – An item that doesn’t require shipping because it isn’t tangible, like a service. It doesn’t have any shipping-related fields at checkout.
- Downloadable – When this option is selected for a product, a new field dynamically appears where you can provide the link to the digital product. When a customer buys the product, that link is provided to them after the checkout process has been completed.
- External – This can also be referred to as an affiliate product. These get listed on your site, and when the user clicks the button to buy it, they’re redirected to the external site where the actual checkout process happens.
- Variable – These are products that have options the customer can select on the product page before checking out. For example, the options could be different sizes for a product such as a t-shirt.
If you use any extensions for the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress, certain ones may also add other product types. You can check out the corresponding documentation for the extension to find out what happens when the new type of product is added in WooCommerce.
Can Orders Be Aggregated on the Main Site?
When you use the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress to create a WordPress online store and you also enable Multisite, you end up with a network of online stores.
If you have a WooCommerce Multistore network, it’s natural to want to be able to manage all of the stores’ products, settings and orders in one place.
Unfortunately, this isn’t possible unless you want to do some custom coding. Or, you can hire expert and verified WooCommerce experts such as those found at Progressus to do this for you.
For details, check out WordPress Multisite and Woocommerce Multisite: An Overview.
Wrapping Up
Running a WordPress online store with the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress can be rewarding. But, sometimes you may have questions about common features. You shouldn’t be shy about asking them.
At least now you have the answers to these three common questions.
Are you still wondering about something? Do you have other questions about managing a WordPress online store or about the WooCommerce plugin for WordPress? Let me know in the comments below.



Hi!
There isn’t an explanation about the users syncing. I mean if I would like registration only on my main site (because I separated the site parts to avoid plugin conflicts) and I have a shop on the main, and a multivendor market on a subsite, the users all data will be available for the sub-market too, and vica-versa the orders data as well to the main profile?
If not, how can II set it up?
Hi David,
By default, WordPress Multisite treats the main site and each subsite as separate. So, users aren’t synced globally, between the main site and the subsites. If you want to sync users for your entire network, you need to use a plugin or custom development for that.
Best,
Jenni